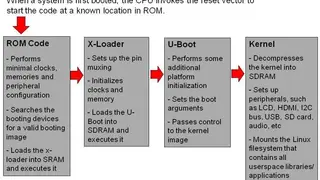
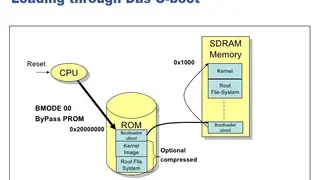
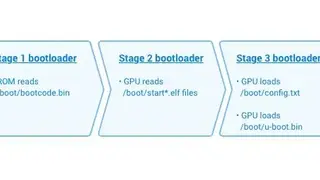
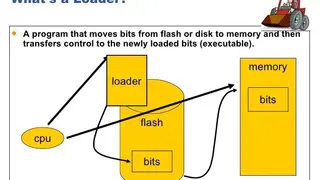
Das U-Boot
Das U-Boot is the first stage and second stage bootloader that can be loaded by BIOS or ROM from a supported boot device like SD card, flash memory, NAND, or SATA drive. If the size is an issue, you can split Das U-Boot into multiple stages. The platform loads a small SPL, which is a toned-down version of U-Boot, and the U-Boot performs at the first stage. The first stage configures memory controllers & SDRAM, and the second stage is booting load modem operating system from many devices that must be configured. U-Boot boots an operating system by reading the kernel and any other required data, e.g., device tree or ramdisk image) into memory, and then executing the kernel with the appropriate arguments.
U-Boot’s commands are actually generalized commands which can be used to read or write any arbitrary data. By using these commands, the data can be read from or written to any storage system that U-Boot supports. U-Boot does not need to read a filesystem in order for the kernel to use it as a root filesystem or initial ramdisk; it simply provides an appropriate parameter to the kernel and copies the data to memory without understanding its contents.
Das U-Boot Alternatives
#1 Clover EFI Bootloader
Clover EFI Bootloader is a software utility that allows you to boot up multiple operating systems with BIOS or UEFI firmware. The tool is made for old hardware systems that don’t support cross compatibilities of UEFI and BIOS. The Clover EFI Bootloader lets you run UEFI operating system even on BIOS only motherboard. The program supports macOS, Linux, and Windows. The customized version of macOS, i.e., Hackintosh, can also be installed on an Intel-based system with the help of Clover EFI Bootloader. You can customize the GUI, personalize icons, themes, fonts, wallpapers, and controls using function keys on the keyboard.
Additionally, you can create custom boot entries for personalizing boot entries and add support for other operating systems. It can boot up to 3 OS and two firmware types at a time. The only con is the complication of emulation and operation. All in all, the tool is made for those who want to use other OS on their officially restricted machine.
#2 GNU GRUB
GNU GRUB is a Multiboot boot loader that is originally derived from the project Grand Unified Bootloader. It is among the first few programs that run when a computer starts. The software is responsible for transferring and loading the controls to the current operating system kernel software like Linux or The Hurd. The kernel, in response, initiates the remaining operating system. The basic functions are for the end-users along with the rich functionalities to support kernel designers and experts. GNU GRUB has backward compatibility for booting FreeBSD, OpenBSD, NetBSD, and Linux. The proprietary kernels like Windows NT and DOS are supported via chain loading functions.
It supports a wide range of operating systems, including GNU/Linux, BSD, Solaris, as well as Microsoft Windows. In addition, it can be installed on Master boot record (MBR), GUID Partition Table (GPT), and Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). Other features are recognizing multiple exe formats, support non-Multiboot kernels, multiple modules, menu interface, flexible CLI, automatic decompression of data, independent of drive geometry translations, logical block address mode, network booting, and remote terminal support.
#3 Systemd-Boot
Systemd-Boot, formerly known as Gummiboot, is one of the simplest UEFI boot managers that lets you boot Linux and Windows in EFI mode even if the system is BIOS only supported. It automatically detects bootable images, including Linux kernel images, operating systems, and other boot loaders. These do not require a configuration file, provides a basic menu-based interface, and can also integrate with Systemd to provide performance data. Systemd-boot reads simple and entirely generic boot loader configuration files; one file per boot loader entry to select from as all files need to reside on the ESP. To install the Systemd-boot EFI boot manager, first make sure the system has booted in UEFI mode and that UEFI variables are accessible.
#4 LILO Boot Loader
LILO stands for Linux Loader, is a boot loader tool that is used to load Linux OS into memory. It allows you to boot the operating system from floppy disk and hard disks without being dependent on the specific file system. Lilo handles some tasks such as locate the kernel, identify other supporting programs, load memory, and starts the kernel. Lilo reads this configuration file, and it tells the OS where it should place the bootloader. The main advantage of LILO is the fact that it allows for a fast boot-up of Linux when installed in the MBR.
The BIOS performs some initial tests when a computer is powered up or restarted with LILO and then transfers control to the MBR where LILO resides. Normally LILO is initially configured for you during the Linux installation process. However, the default configuration might not be correct, and you will have to change it. All in all, LILO Boot Loader is an old-school tool for running the latest OS on old machines.
#5 Windows Boot Manager
Windows Boot Manager software is a part of the volume boot record that loads from volume boot code. It allows you to bot Windows operating system including 7, 8, 10, and Vista. It is a default boot manager for every Windows OS, and the configuration file name BOOTMGR can be found in the Boot Configuration Datastore, which is like a registry database. Windows Boot Manager replaced the boot.ini file used in older versions like Windows XP.
The Windows Boot Manager file is hidden and read-only by default located in the root directory of the partition. The partition is marked as a system reserved in most cases. The boot manager cannot be disabled but can be set to one operating system in the Administrative Tools. This action reduces the Windows boot time effectively.
#6 BootX
BootX is a boot loader software developed by Apple that was a part of macOS in Macintosh computer machines. Just like Windows Boot Manager, it helps macOS and all required device drivers to boot in the memory. The ROM computer chip that contains Open Firmware uses a graphical bootsplash compatible with Macintosh computers. The startup sequence starts with the Apple logo with the spinning cursor. Apple added some features to allow flexibility in the booting process, like network boot using TFTP and load ELF or Mach-O formatted kernels.
BootX can also be booted from USF, ect2, HFS, and HFS+ formatted volumes. You can manipulate the bootloader at startup with multiple key combinations to manipulate the booting process. For example, the Verbose mode can be activated but holding down the Command plus V key at the startup. This action replaces the Apple logo with text-based information.
#7 Darwin Bootloader
Darwin Bootloader is used to load additional kernel extensions from RAM supplied by a Multiboot loader. The ramdisks are supplied in the form of Multiboot modules. In order to function properly, the ramdisks must be in flat format with a partition table like MBR, GPT, or APM along with HFS and HFS+ partition. One thing to note that the archive of the extension from the ramdisk is loaded in addition to the extension archive on the boot volume. For example, you might place ACPIPS2Nub and the ApplePS2Controller extensions on the ramdisk and add support for PS/2 devices.
You cannot provide modified versions of existing extensions on the boot volume or cause the booter not to load the extensions on the boot volume. However, if you use Darwin Bootloader correctly, it is fully capable of booting an unmodified OS X Leopard DVD. To do so, you merely need to provide whatever extensions you need to make OS X work in your initrd file.
#8 Reboot to recovery/Bootloader (root)
Reboot to recovery/Bootloader (root) is an android app that takes you to the boot recovery menu with one click. In order to function, the Operating system must be rooted first as the app uses command lines. You can directly go into the recovery menu, boot menu, fast boot mode, flash a custom ROM, kernel, and tools into your Android OS. The app eliminates the hassle of finding the recovery boot method and key combinations to enter the menu. Just select where you want to go, and it will take you there after restarting the phone.